Paging Erin Brockovitch
Lipid impurities: Volatile halogenated solvents, toxic metals and more
In my quest to really understand the lipids and for this well, chapter, I am writing (84 pages and counting!) I dug into the lipid manufacturing steps and what the EMA hack/leak said about it.
ALC-0315
This is the ionizable lipid. It was made by Avanti Polar Lipids and for Europe, the manufacturing process was transferred to Croda Europe. Then scaled up for commercial production. So now they need to make kilograms of this stuff instead of just milligrams.
Here is Avanti Polar Lipids (in Alabama) together with Croda. You can read all about their new targeted lipids, which is a PEG lipid.
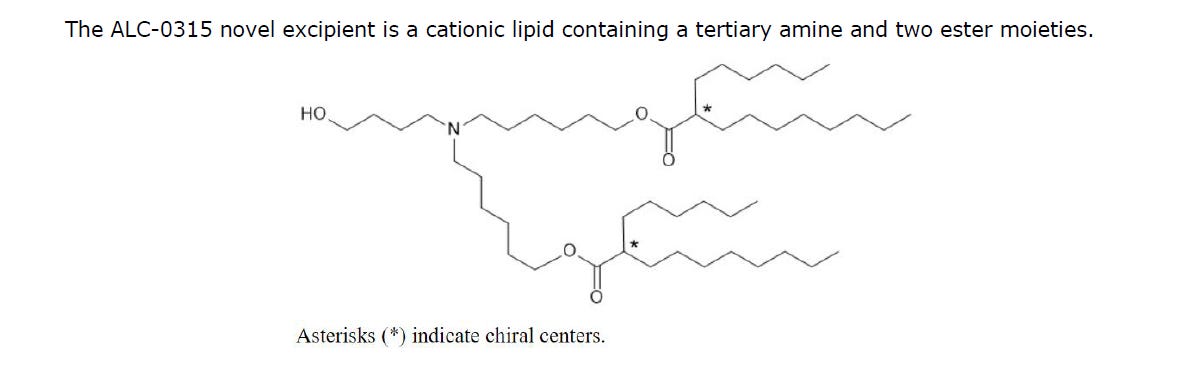
Structure of ALC-0315
You can see 2 chiral centres which as Geoff Pain says, is never mentioned again. All I can find is that entaniomers may make a difference in the ability to cross the cell membrane but that’s it. And it is not specific.
Pfizer told the EMA the steps in making ALC-0315 but the purity was hard to measure since lipids don’t really have chromophores so figuring out impurities was difficult, especially for the organic impurities. They had to develop a new analytical test which was HPLC with a charged aerosol detector (CAD). So they were pretty serious about the organic impurities. Probably because they weren’t mutagenic.
But HOLD ON. Making these lipids require HALOGENATED VOLATILE SOLVENTS. Look here.
See those residual solvents? Well dichloromethane also known as methyl chloride is a CLASS 3 mutagen (Benzene is a Class 1 mutagen). Methyl chloride is mutagenic and genotoxic in vitro but equivocal in vivo. Luckily most of these are volatile and are removed through vaccuum drying.
BUT, do you see that Pfizer/BioNTech is proposing Not More Than (NMT) 5% impurities total, and that individual impurities are pending? What does that mean. Well 5% impurities (95% pure isn’t all that pure) is NOT usually accepted for pharmaceutical products. You are aiming for at LEAST 97%, preferably 99% pure. PLUS, you could have one or two impurities which are very toxic, and have the final product at 95% purity.
Pfizer plays its usual card.
Note:
lifetime exposure predicated on 2 doses only (i’m sure booster doses were already being planned for)
21.5ug total impurities may not really be that small depending on the toxicity of the impurity
Setting specifications on batch data could lead to supply issue IN A PANDEMIC, OMG WE CANT HAVE THAT.
My antenna is tingling. HMMMMMM
Elemental Impurities
Ok THIS is where it gets weird. There are a lot of metals and elements in the lipids from the manufacturing process. Here is a list Pfizer provided.
OK what do you see? All kinds of stuff like ARSENIC (As), ANTIMONY (Sb), VANADIUM (V) plus the usual lead, mercury, nickel etc. All are at <25% of the acceptance criteria by the ICH Q3A which are the standards for impurities in new drug substances ICH M3. Technically they meet the overall standard.
BUT JUST WAIT A MINUTE. Do you see “SOME DATA ARE PRESENTED” in the table. What about OTHER data that is not reported? And see only one batch of the Croda manufacturing is provided.
The Manufacturing Patent Used Hexavalent Chromium
So, reading about the manufacturing of the lipids I come across this paper.
And then my eye fell upon THIS
HEXAVALENT CHROMIUM!!!!!
You may remember that this was the chemical because of Erin Brockovich. She became instrumental in suing the utility company on behalf of the town. The case (Anderson, et al. v. Pacific Gas & Electric, file BCV 00300) alleged contamination of drinking water with hexavalent chromium (also written as "chromium 6", "chromium VI", "Cr-VI" or "Cr-6") in the town. Erin Brockovich Wikipedia
Cr(VI) it is a known carcinogen and may have genotoxic effects due to formation of DNA adducts, which can lead to DNA damage. Here is a paper I need access to because it talks about the MITOCHONDRIAL effects, ROS and DNA adducts, all the stuff I have been looking at regarding the toxicity of the LNPs. Plus cardiotoxicity of course.
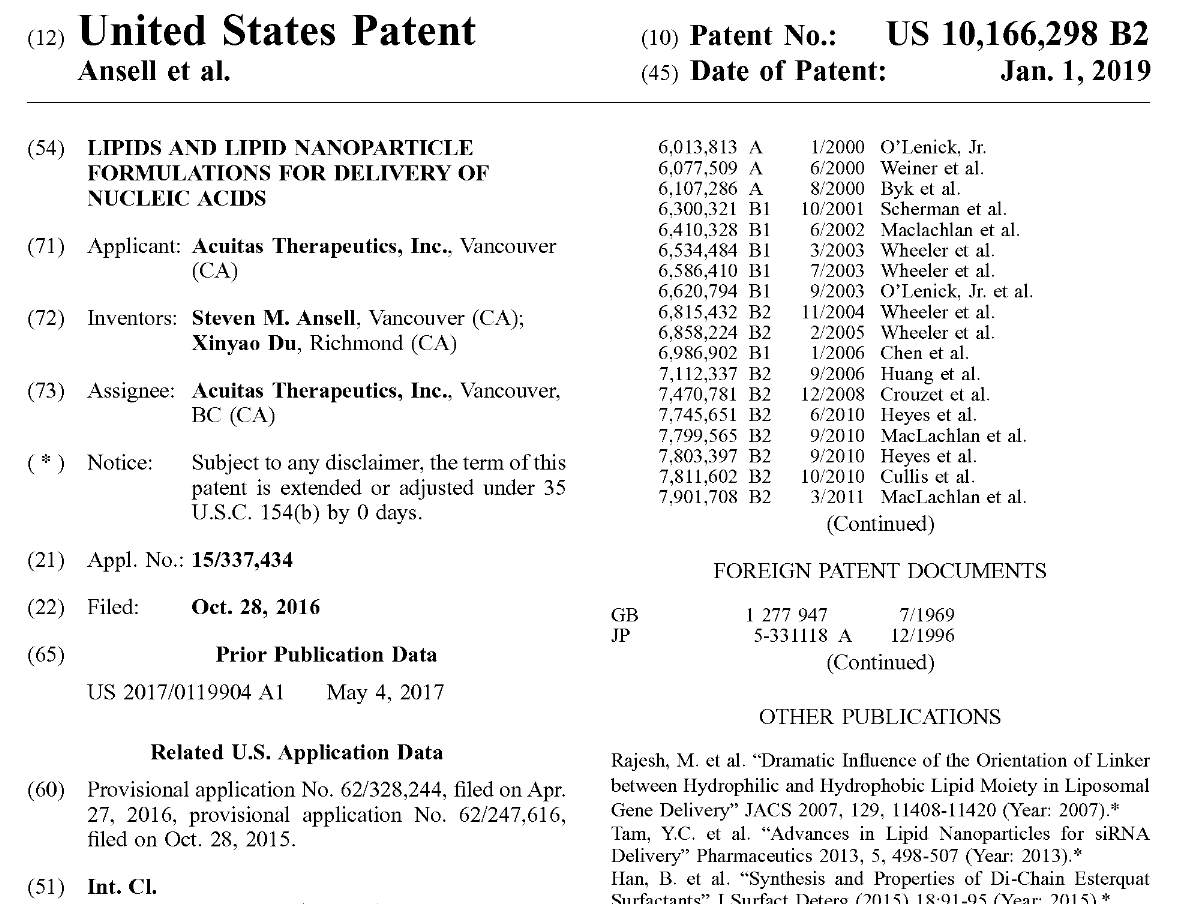
The Patent
The public domain route is the patent found here.
As we can see this is Acuitas Therapeutics from Vancouver who has patented the manufacturing method to make ALC-0315. Date Jan 1, 2019, though there appears to be an earlier patent. I am having trouble finding Cr(IV) in the patent but I guess it is part of a toxic reagent Cr(iv) in pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), and PCC is mentioned in the patent. So it is likely this was the methodology used to make ALC-0315 in 2020 when the vaccines were first being manufactured.
The New Method (Saaditi et al)
This paper is worth reading because it is very well written and you don’t need to understand much chemistry and still understand the basics. And it made me laugh. Here is what he writes about the manufacturing process of making ALC-0315 that is in the patent.
OOOF, tell me how you really feel Dr Saadati. What is really interesting is that this Dr Saadati works at, you guessed it, the University of British Columbia in Vancouver. Me thinks he knows Pietr Cullis indeed.
This was published in July 2022 so your guess is as good as mine on whether this method with no Cr(IV) is currently being used in making ALC-0315. He has his own patent of course published Nov 2023 by a company called Nanovation. Located on the campus of UBC. Ahem. Saaati patent
These lipid patents are looking more convuluted every day.
How Toxic is Hexavalent Chromium?
Hexavalent chromium is considered an occupational hazard. All hexavalent chromium compounds are considered carcinogenic to workers. The risk of developing lung, nasal, and sinus cancer increases with the amount of hexavalent chromium inhaled and the length of time the worker is exposed. Mostly stainless steel production, leather tanning, electroplating, and industrial process like making synthetic lipids I guess.
Chromium, in the form of trivalent chromium Cr(III) is an essential nutrient for the body, but Cr(IV) is toxic. Details matter in chemistry, which is why I like it, lol.
Under the current guidelines (EPA, 1986), Cr(VI) is classified as Group A - known human carcinogen by the inhalation route of exposure. Carcinogenicity by the oral route of exposure cannot be determined and is classified as Group D.
But this is not an inhalation exposure or an oral exposure. It would be contained in the LNPs and then transfected across the cell membrane. But hexavalent chromium crosses the cell membrane very easily on its own. I think the risk would be closer to an inhalational exposure.
SO HOW MUCH HEXAVALENT CHROMIUM is in AL-0315?
Maybe the Material Data Sheet will tell us?
Guess not. Maybe this is the clean method? Note the 0.1% figure. So Avanti is >99% pure. But I don’t think that matters much if it is even 0.5% Cr(VI) or in ppb (parts per billion).
What are the limits by Occupational Health Agencies? The EPA has a level of 0.1 milligrams per liter (mg/l) or 100 parts per billion (ppb) in water. That would be
0.1ppm
That is a pretty low level.
see EPA Chromium in drinking water
But I cant seem to find anyting for IM or IV administrations because really, when would THAT HAPPEN? And the inhalational exposure limits aren’t very helpful because it is particulate per cubic litre of air. Nonetheless, even if we used the levels allowed for in water, is there is a chance hexavalent chromium is present at >0.1ppm if we look at what the other elements present and their levels in ppm?
Given the small amounts of lipids given, it is unlikely the levels of hexavalent chromium is at a very high level. Nonetheless, it shouldnt be there if at all possible. AND DID PFIZER HIDE THIS FROM THE REGULATORS AS WELL?
We need someone to test these lipids for metals.
Summary
the lipids themselves have impurities
some of those impurities are known carcinogens
hexavalent chromium is used in the production of AL-0315
it is not known if the published patent method is the one currently used to make ALC-0315
The amount of hexavalent chromium in the LNPs is unknown
can we get Erin Brockovich?
Thanks for reading
And pray the rosary











To quote you, Maria, Holy Toledo!!!
Multiple myeloma was the result of chromium exposure from years of electroplating.