Much of the stuff I have been looking at regarding manufacturing defects and linking to adverse effects are related to the analytical methods used to determine quality and purity. We reviewed the critical quality attributes in my previous post, now we we look at the analytical methods itself.
How is 'Quality and Purity' Measured?
Just before the ‘pandemic’ hit in 2020, I was working as a pharmacy consultant for a smaller hospital pharmacy who had been ignored and poorly managed for many years. One task I had was to help establish policy and procedures for sterile compounding including hazardous (chemotherapy) compounding in a new clean room. The manufacturing we do in hospital i…
Compendia, Compendial, Compendium
A compendium is a compilation of knowledge about a particular subject (“compendia” is plural and “compendial” is an adjective). These terms are now mostly used for drugs and medication.
Back at the turn of the last century medicines were mostly made without consistency by individuals in apothecaries; the dosing levels and the quality of the ingredients often varied greatly, which could harm patients. And so quality standards were established to ensure quality and purity. Over the years this knowledge has been compiled into compendia which are used by drug manufactures, regulatory bodies (e.g. for pharmacy, veterinary) and are often referred to a “pharmacopeia.” Every country has designated at least one pharmacopeia for consistent drug manufacturing. The most comprehensive and ones used throughout the world are:
USP-NF (United States Pharmacopoeia and National Formulary) which is a merging of the US Pharmacopoeia and British National Formulary (which was used by Canada)
Ph EU ( EU Pharmacopoeia standard) established within the context of modern manufacturing and regulatory systems in Europe
Japan
Compendial Standards
These are standardized protocols for many pharmaceutical raw materials and finished products. Testing and compliance to these standards detailed within compendial methods is a basic requirement for global manufacturing, release and distribution of pharmaceutical ingredients and drug products.
Testing and Regulatory Guidelines
Role of Pharmacopoeia Organizations
So what is the role of these organizations such as forr instance USP, with which I am familiar? These organizations which maintain pharmacopeoia are non-profit private scientific organizations that disseminate quality standards. These include MONOGRAPHS and are organized in CHAPTERS. Chapters are designated by <number>. USP has no role in enforcement; that is left to FDA and other government authorities in the U.S. and elsewhere.
Furthermore, you need to BUY their standards (on line now) which runs about $700-800 for hospital pharmacy for example. BTW, every hospital pharmacy in Canada are required to own this document but sometimes the hospital administration refuses to pay for this (ask me how I know).
So USP sets up the standards and the methods but the actual enforcement and limits are upto the FDA/EMA etc. This is especially important to understand for the mRNA jabs
What Do These Standards Look Like?
So what do these standards look like? Lets look at measuring residual DNA in biological drugs.
USP Standard for qPCR for DNA
USP reference Unfortunately you need to be a subscriber to get the entire standard but the overall reference is in the pdf above.
As you can see, there is NO value that must be obtained, this is ONLY the analytical methodology. However, these are very detailed and very precise methodological standards with standardized reagents (which you also need to buy, lol)
What USP or Pharmacopoeia Standards Were Available for the modRNA Jabs?
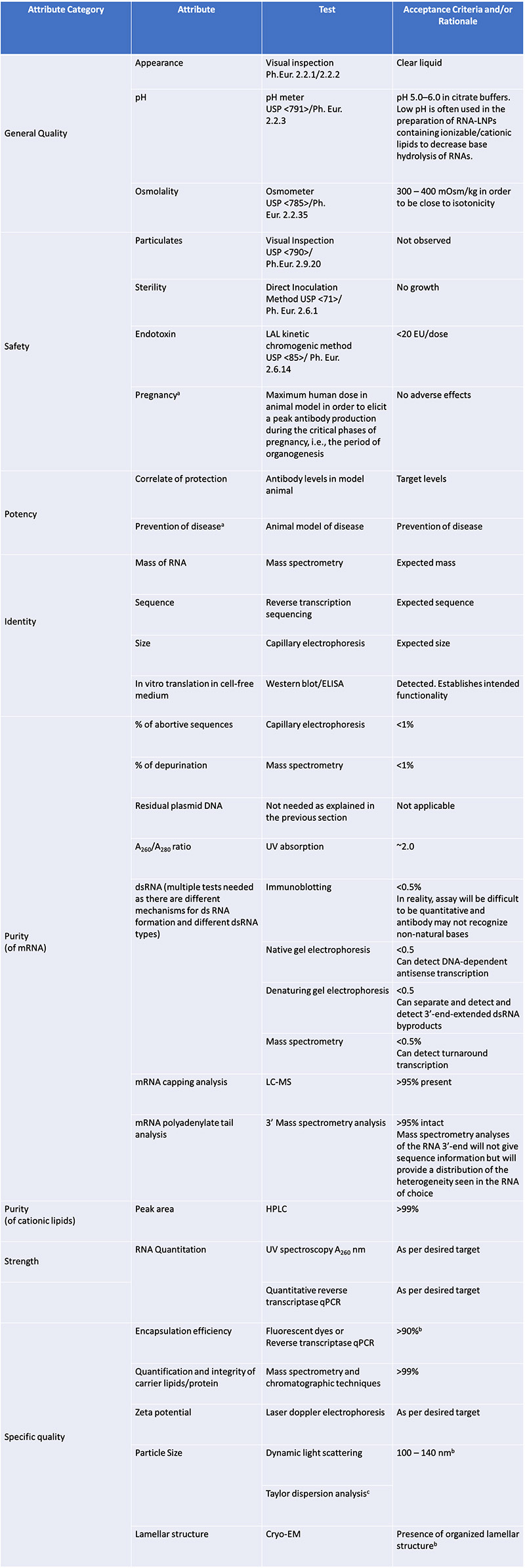
Well, as we can see from the previous post, the compendial standards that were used for the mRNA jabs for the DRUG SUBSTANCE (ie the modRNA only) was
residual DNA testing using qPCR
endotoxin testing using LAL
bioburden using colony forming units (growing out bacteria/yeast on agar plates etc)
appearance
clarity
pH
All of these standards have USP Chapters and are standard for most IV medications and have been for many many years. And all except for rDNA also have Limits or Values since these have been established for all IV medications for 20+ years, maybe more. There are conversations about the appropriateness of endotoxin testing with LNPs etc as there is for rDNA testing for the same reasons. But there ARE compendial standards at least.
But there were no compendial standards for
RNA content: UV spectroscopy was used. This is what Kevin McKernan is talking about. Using qPCR for DNA which is compendial but a less sensitive method for RNA content because there is no standard. Is it the right analytical method? How robust does it need to be? Then secondarily what RNA content is sufficient as determined by the FDA?
RNA identity: here PCR is used. But only to identify it is the proper RNA. No sequencing for example.
RNA integrity: capillary gel electrophoresis. Is this appropriate? Sufficient? This is where 55% or more full intact RNA integrity came from. That is the FDA/EMA and Pfizer/BioNTech agreement (cough, cough) but is the analytical method itself appropriate? Should there be additional tests?
dsRNA: immunoblot. Now this is another rabbit hole and the EMA in particular had issues with using this analytical method for measuring dsRNA.
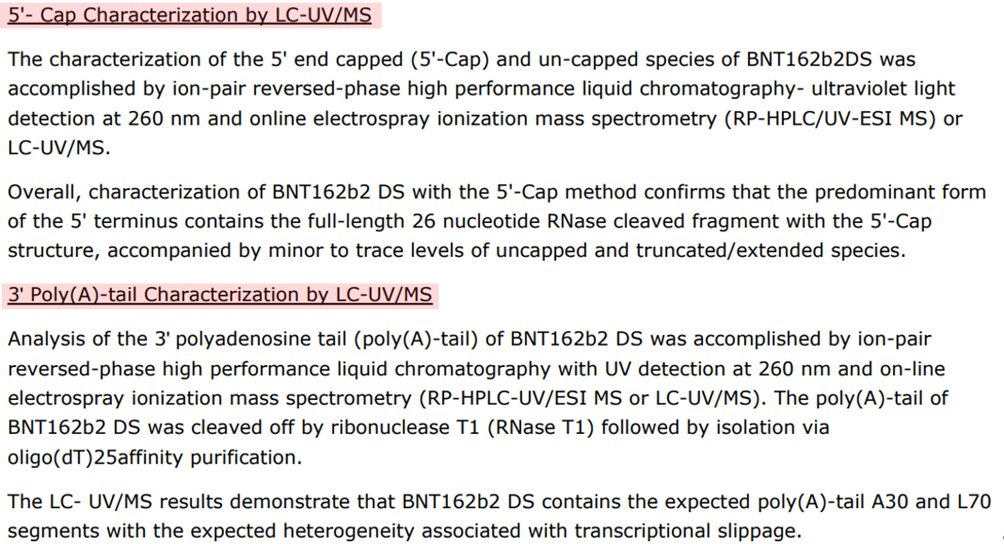
Poly(A) tail: ddPCR. Another BIG issue. Is it appropriate? I can find no one using this analytical method to determine polyA tail length/distribution. There was a cryptic comment in the rolling review by an analyst who noted regarding the ddPCR …this is not understood.
5’cap using RP-HPLC
The fact that there are no compendial standards is in and of itself, not surprising. It is a new platform. BUT it really disturbs me when scientists say this platform has been studied for AGES. But the appropriate compendial standards have not been defined. Usually this takes a few years in the process of development of a new product as both the manufacturers and the regulators are learning about what is required for quality and purity. Of course with Warp Speed this was not done
As a result, many impurities and inappropriately used analytical methods was perhaps used to “fake” the quality and purity. And in the case of the dsRNA and polyA tail in particular, unusual and not generally accepted analytical methods have been used. This has bothered me greatly since these manufacturers have the ability and the money to use state of the art methods. ARE THEY HIDING STUFF?
The Analytical Methods were Changed Between Process 1 and Process 2
Patent Sun on X brings up and important point. When Process 1 was compared to Process 2, highly specific and sophisticated analytical methods were used for the 5’cap and the Poly(A) tail, taken from the rolling review.
HOWEVER, for the Critical Quality Attributes or for regular testing of the Drug Substance for lot release, the analytical method was changed, supposedly for speed and ease. Look carefully at what was changed.
Sequencing of the starting DNA plasmid NO LONGER required.
But RT-PCR of RNA sequence was required. Though the primers could be just for a specific region. Others may comment.
Identity of RNA length via AGE not required
The 5’cap and poly(A) tail analytical tests were HPLC-UV and ddPCR respectively. I am not certain, but this table implies these were not measured routinely for the Process 1 vials. However, process 1 and process 2 were compared using the techniques as mentioned above. This is my read of the rolling review. Because these analytical methods were so different, I have always wondered if there is something going on with the 3’UTR regarding the poly(A) tail methodology. Comments welcome.
What Others Are Recommending for Appropriate Analytical Tests for Purity and Quality of the modRNA Drug Substance
Please see My previous post on dsRNA
Note the issues with dsRNA but the multiple analytical methods used.
Implications
The USP has published some draft guidelines for new compendial standards for mod RNA jabs and that is a welcome initiative. BUT, we do not know what the actual LIMIT OR VALUES that will be used to ensure quality by the regulatory authorities?
The lack of standards and robust analytical methods, plus the the determination of what are the appropriate methods is something that needs more analysis. Residual DNA is just the start.
The manufacturers have the means and ability to make these products purer and of higher quality, but it is likely these can never be made to the purity required to ensure no adverse off target effects are not seen with any impurity or contaminant. And it looks like there is no incentive to do so for these particular jabs. This is why we need to determine if there has been any change with the XBB vials in more detail.
The fact that the robustness and the analytical methods CHANGED between process 1 and 2 needs more analysis. Why was this done? What are the implications?





An essential reading for everyone before you feel the need to criticize (for or against, irrelevant). This should be a mandatory part of all informed consent forms, explained in layman terms.
I find it interesting that in the realm of human health/life, which is loudly advertised as the most important thing in the universe, you will be forced to apply a certain set of rules AND forced to buy these rules at a rip-off price. It’s a nice way to build a comfy nest for friends and friends of friends. But… where is Greta? It is anti-ecological beyond comprehension. 50 years after the introduction of computers to the public, and you still need to buy a non-centralized document? Apparently, the manager of these valuable papers cannot build a minimalistic online repository for 50 forms… What does it say about their practical competencies? The same “buy or else” policy is in place in many fields of technology, unfortunately.